Utilisation of Artificial Neural Network in Predicting Crop Yield Based on Macronutrient (N, P And K) Uptake Rate From The Chilli (Capsicum Annum L.) Treated With Food Waste Compost
Keywords:
Artificial neural network, machine learning, precision farming, composting, nutrient management, food waste compostingAbstract
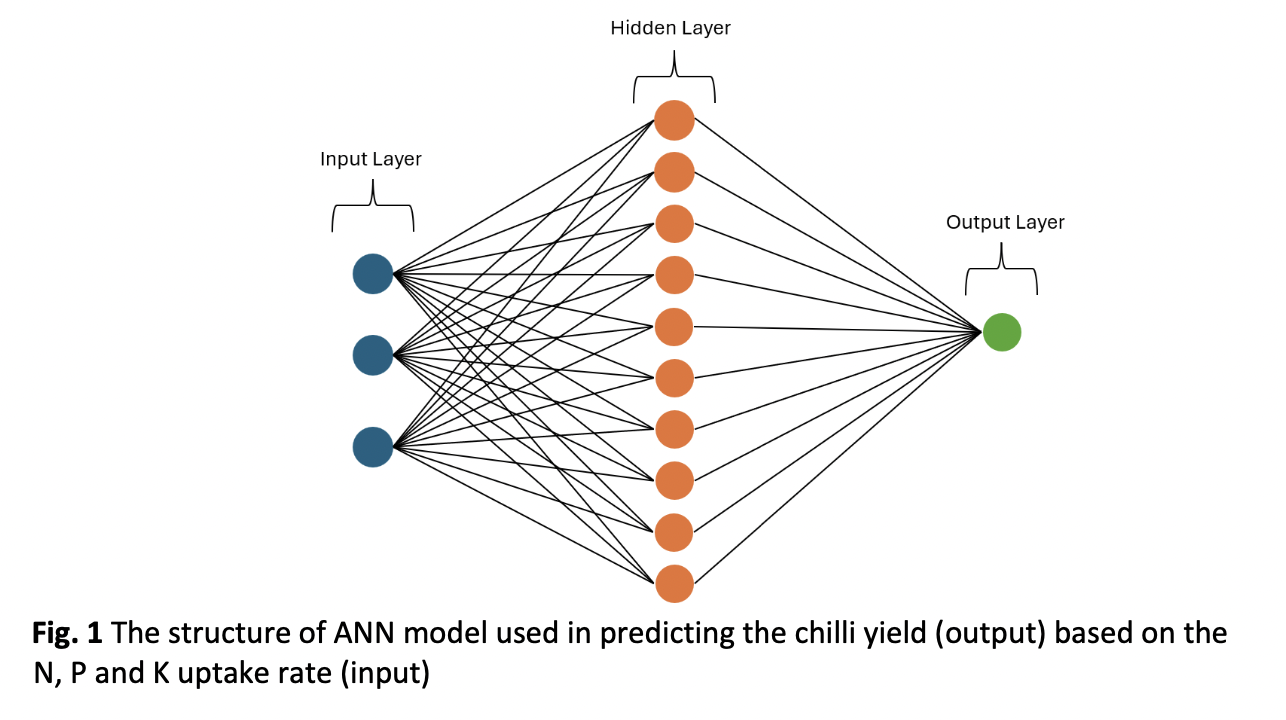
Food waste compost provides essential macronutrients (N, P, K) for chilli cultivation, but its inconsistent nutrient composition complicates precise application rate determination for optimal yield. To address this challenge, this study developed an artificial neural network (ANN) model predicting chilli yield based on plant N, P, and K uptake rates derived from compost applications. Chilli plants were grown under five food waste compost loading ratios (0%, 20%, 50%, 70%, 100% v/v). Leaf tissue were collected during the fruiting stage to quantify the macronutrient uptake rates, while chilli yield (total fruit weight per plant) were determined at day 84 and 112. A 3-10-1 topology ANN model, using N, P, and K uptake rates as inputs and yield as output, demonstrated high predictive accuracy (correlation coefficient = 0.922, RMSE = 11.2731). The 50% v/v compost treatment yielded the highest fruit production (29.58 g plant-1), corresponding to uptake rates of 0.694 g N kg-1, 0.312 g P kg-1, and 0.767 g K kg-1. This ANN model establishes a novel framework for determining site-specific food waste compost application rates based on target nutrient uptake, thereby optimizing chilli yield and enhancing resource efficiency in sustainable agriculture.