Optimization of Pectin Extraction from Pineapple Peel in Acetic Acid Solution via Microwave-Assisted Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sijsfa.1.1.3038Keywords:
Extraction, pineapple peel, pectin, microwave-assistedAbstract
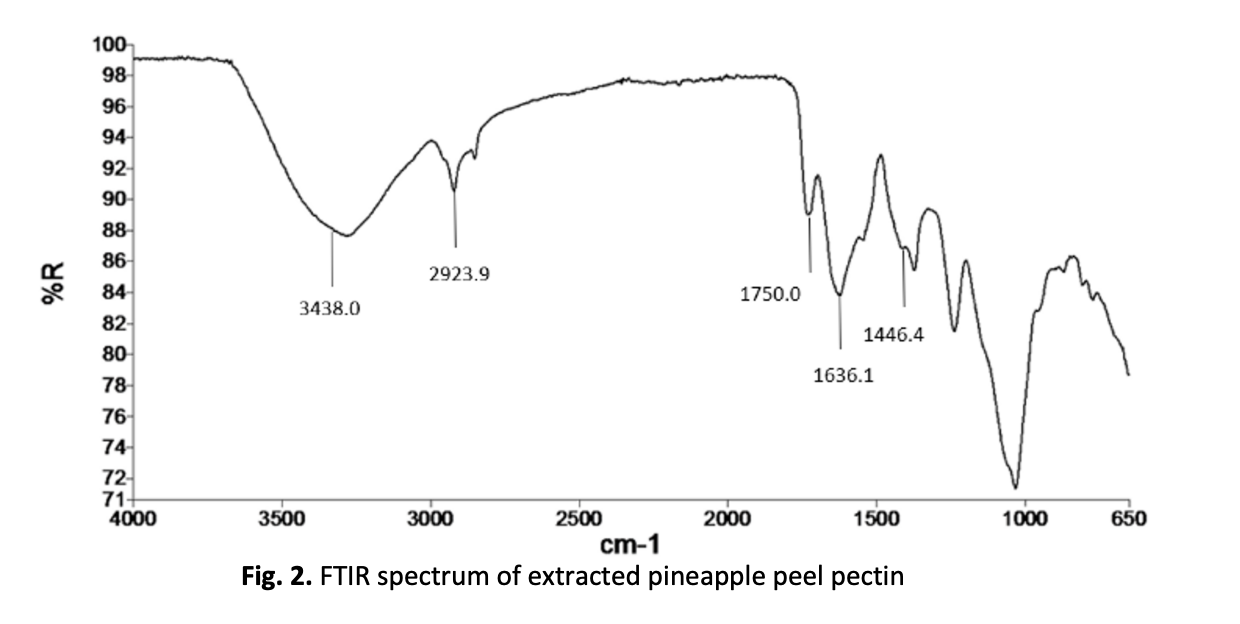
Biowastes from food processing industries, such as pineapple peels, cause environmental issues due to their high nitrogen, phosphorus, macronutrients, and water contents. However, these biowastes also contain valuable bioproducts like pectin, which is widely used in the food industry as a thickener, emulsifier, stabilizer, and gelling agent. Conventional pectin extraction method requires prolonged processing at high temperatures, leading to thermal degradation of pectin molecules. To address this, the current study optimized pectin extraction from pineapple peels in acidic solution using microwave-assisted method. Response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to determine the optimal extractions, considering pH of acetic acid solution (2, 3, and 4), extraction time (2, 3, and 4 min), and microwave power (270, 360, and 700 W). The highest pectin yield (0.53 %) was obtained at 3 minutes of extraction, 270 W microwave power, and pH 4 of the acetic acid solution. The extracted pectin was analyzed for its degree of esterification, and its structural characteristics were compared with commercial pectin using FTIR with KBr method, revealing no significant differences. These comparable characteristics confirm that the microwave-assisted method is an efficient alternative for pectin extraction, offering a faster and more sustainable approach with potential applications in the food industry.